Three automatic orientation modes are available in the toolbar and from the Surface > Auto-Orientation menu:
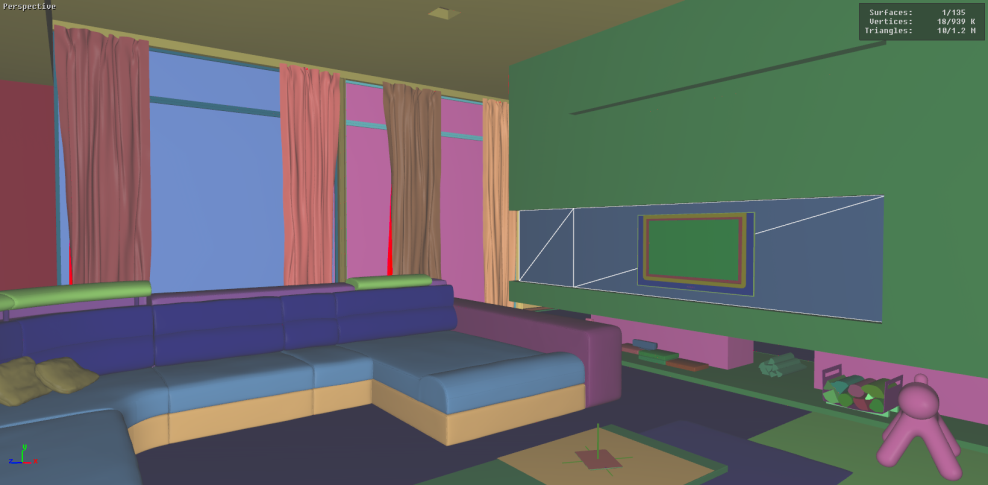
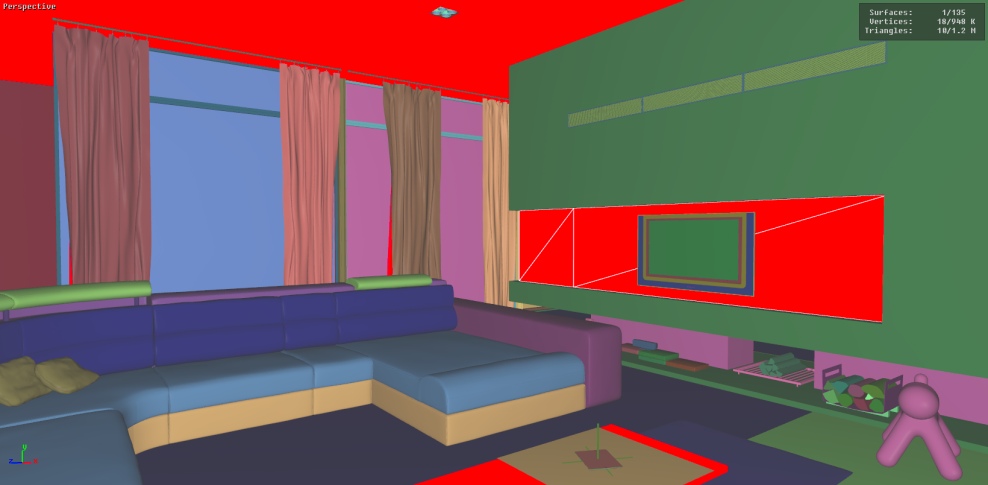
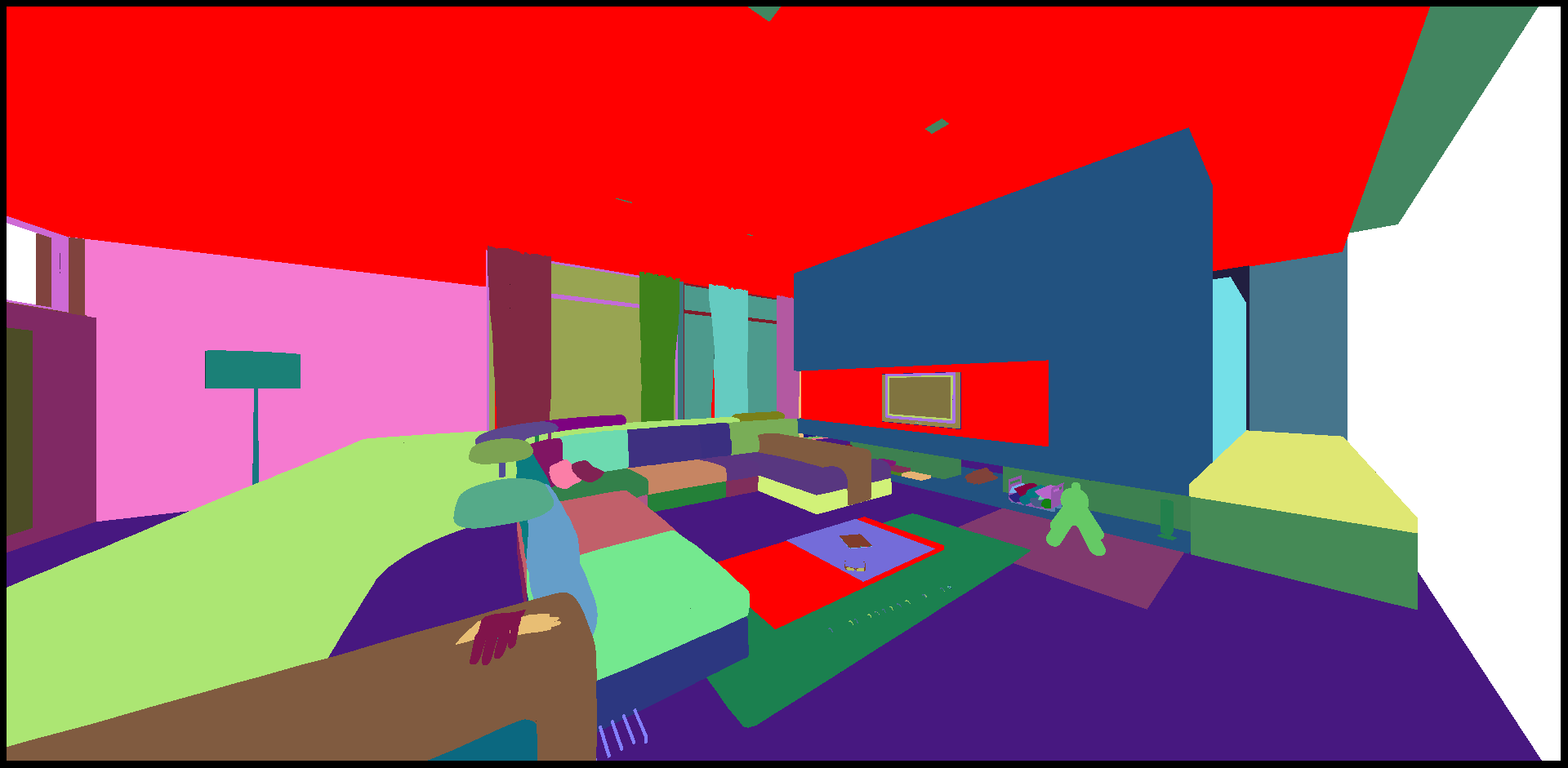
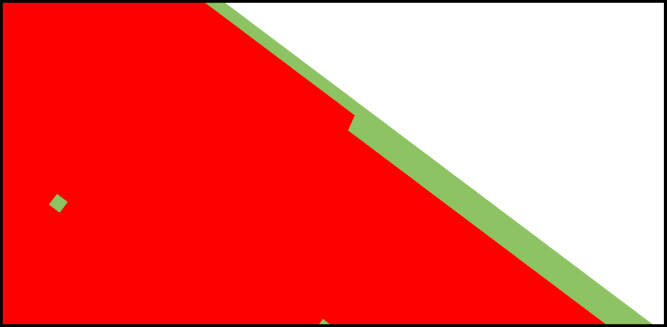
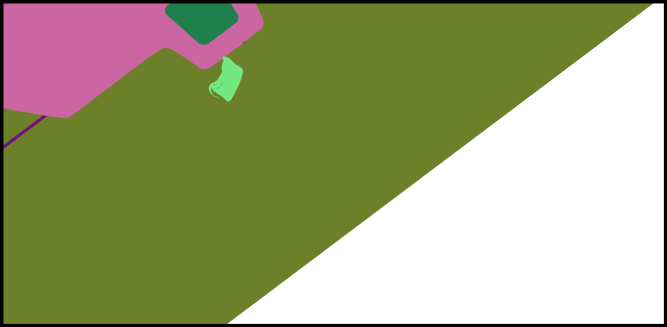
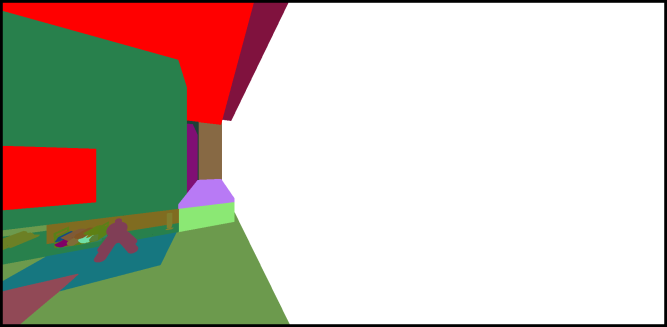
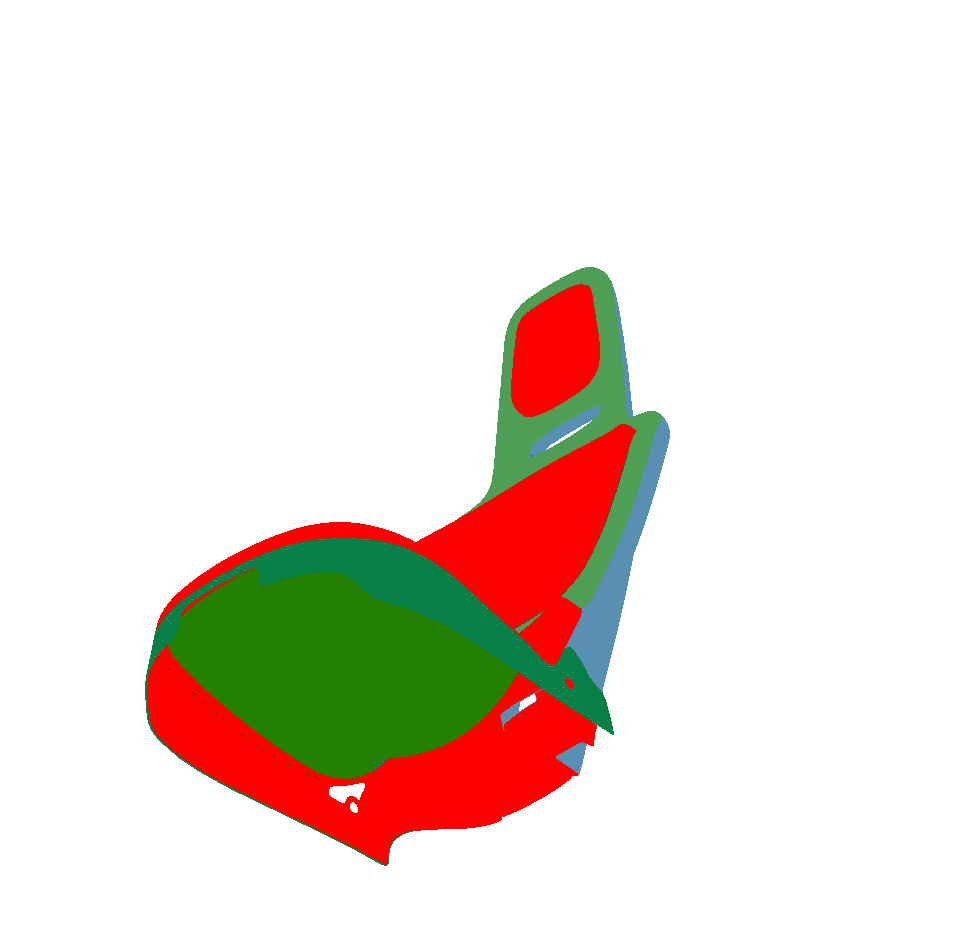
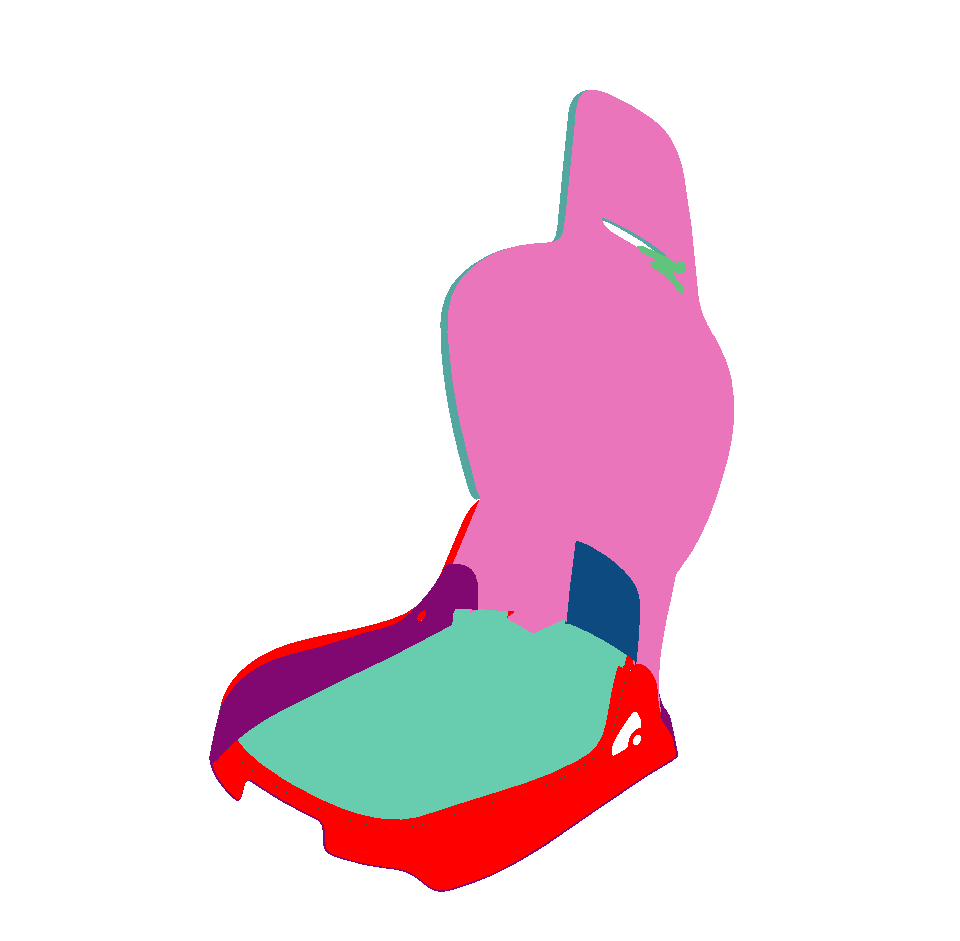
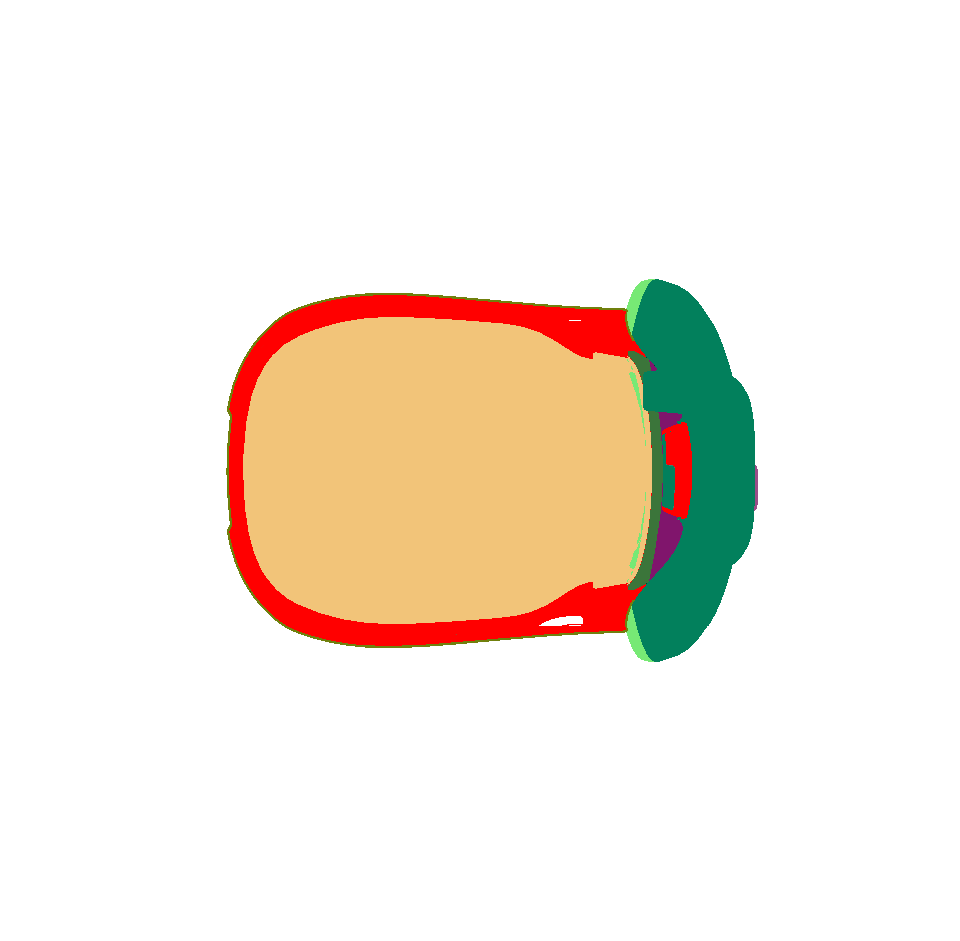
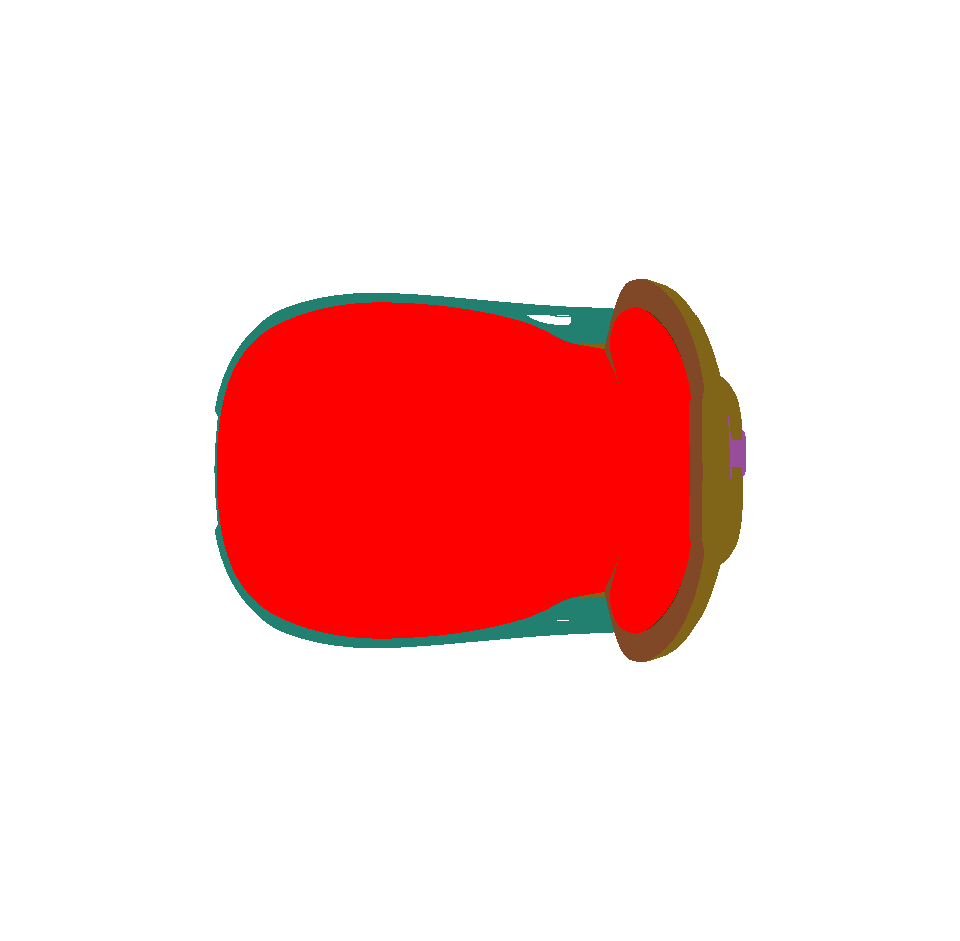
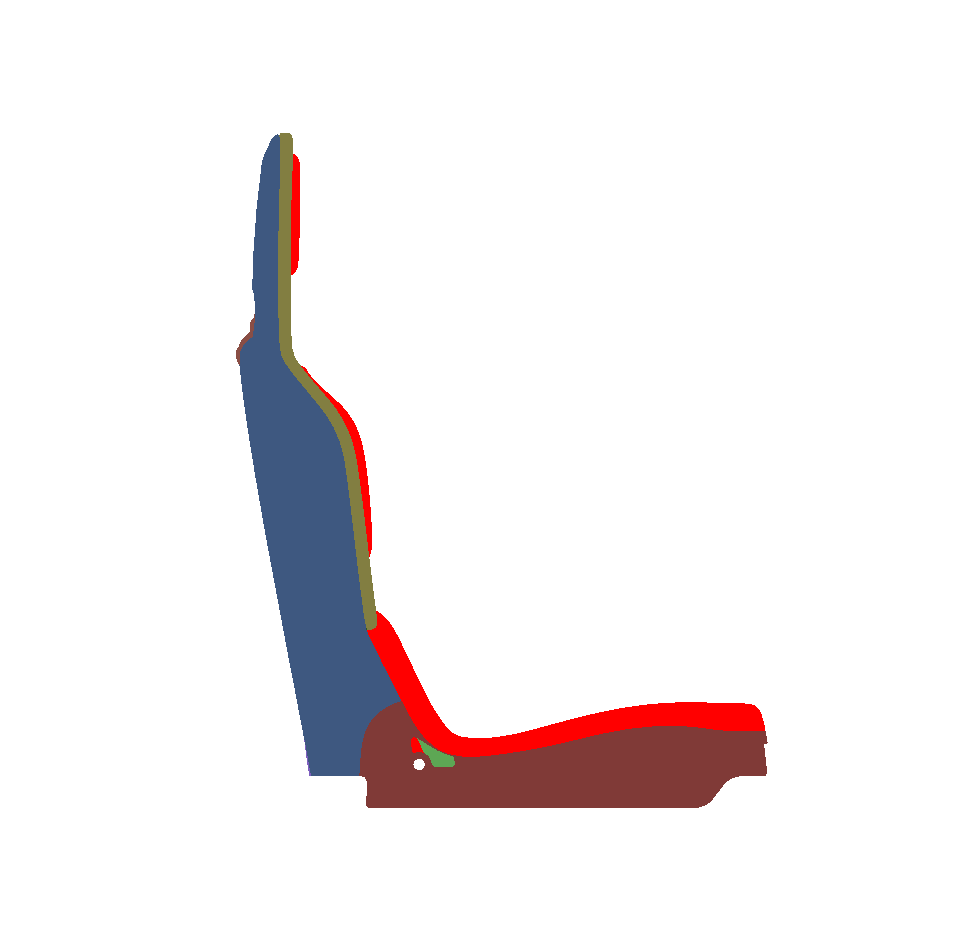
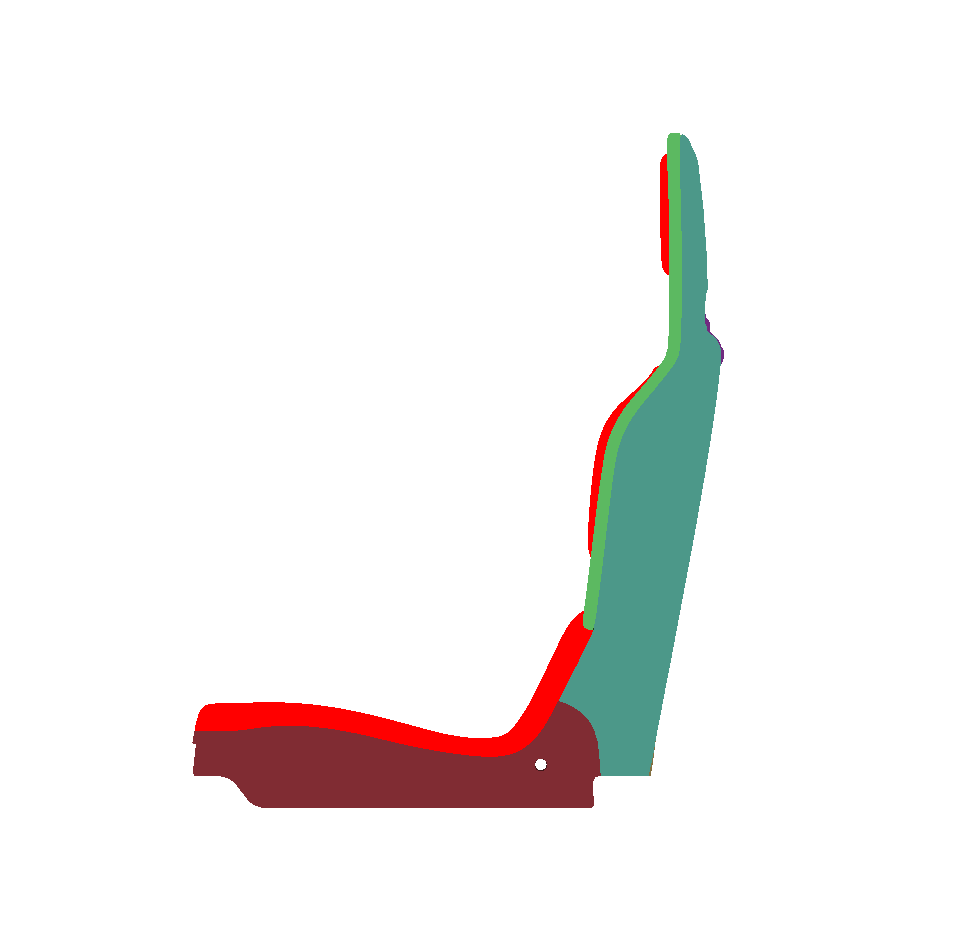
 Visible Surfaces: automatically orients all surfaces visible from the current point of view. In order to determine if the front or the rear face of a surface is visible from this point of view, a rendering is performed. The number of red pixels is compared to the number of pixels of another color among the visible pixels of the surface (i.e. pixels not occluded by another surface). If most pixels are red, the surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Visible Surfaces: automatically orients all surfaces visible from the current point of view. In order to determine if the front or the rear face of a surface is visible from this point of view, a rendering is performed. The number of red pixels is compared to the number of pixels of another color among the visible pixels of the surface (i.e. pixels not occluded by another surface). If most pixels are red, the surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
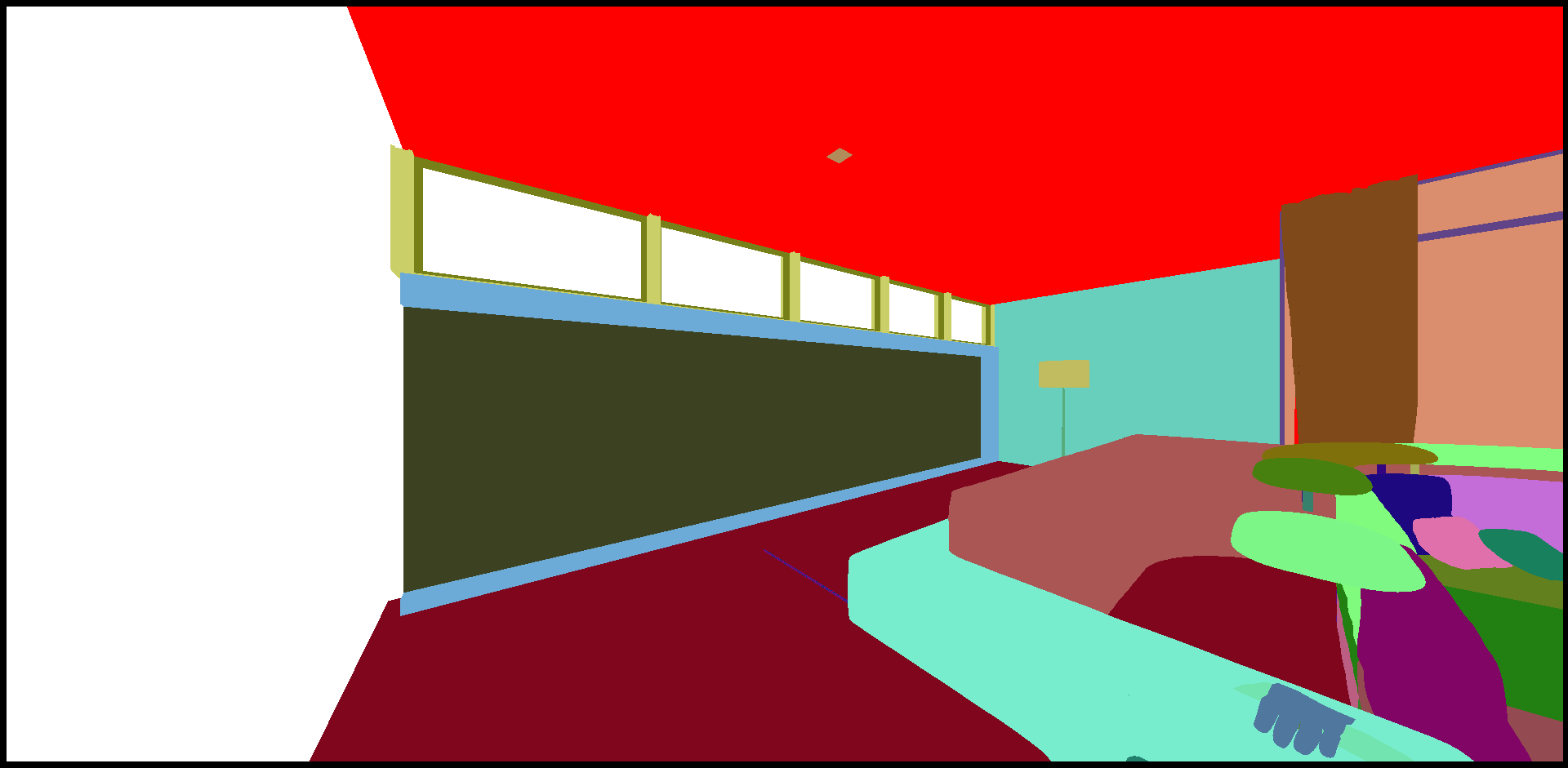
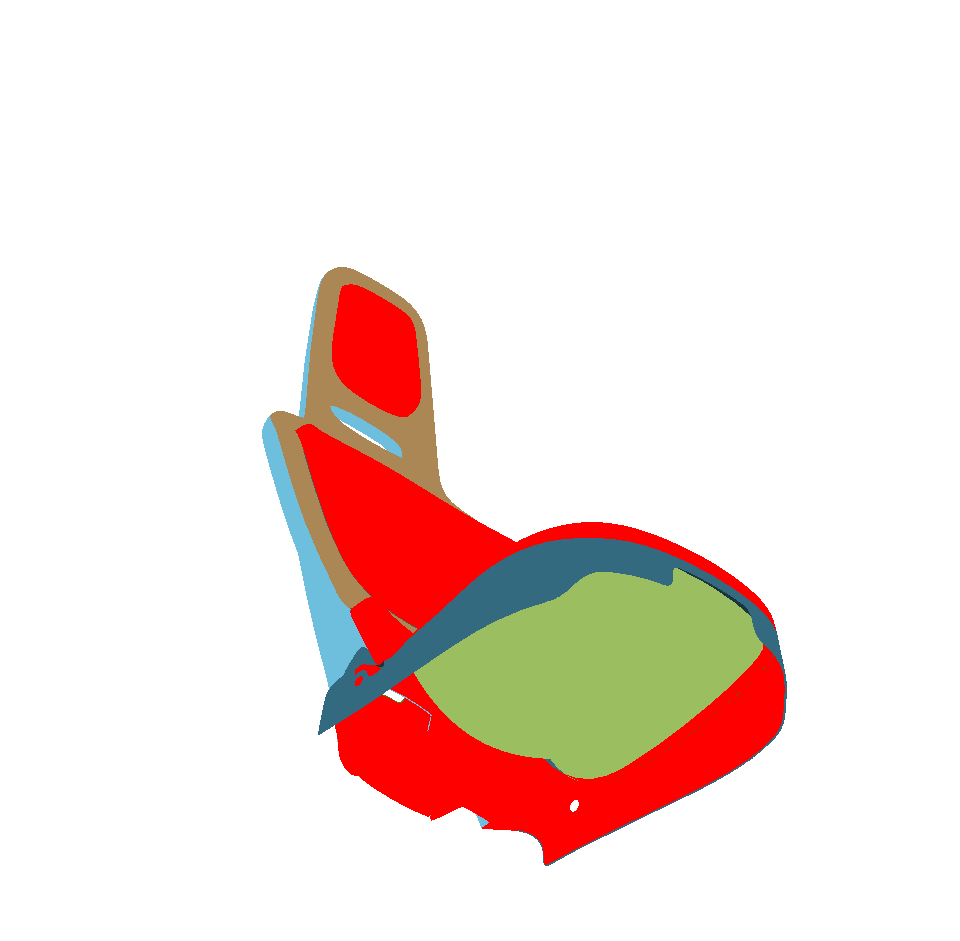
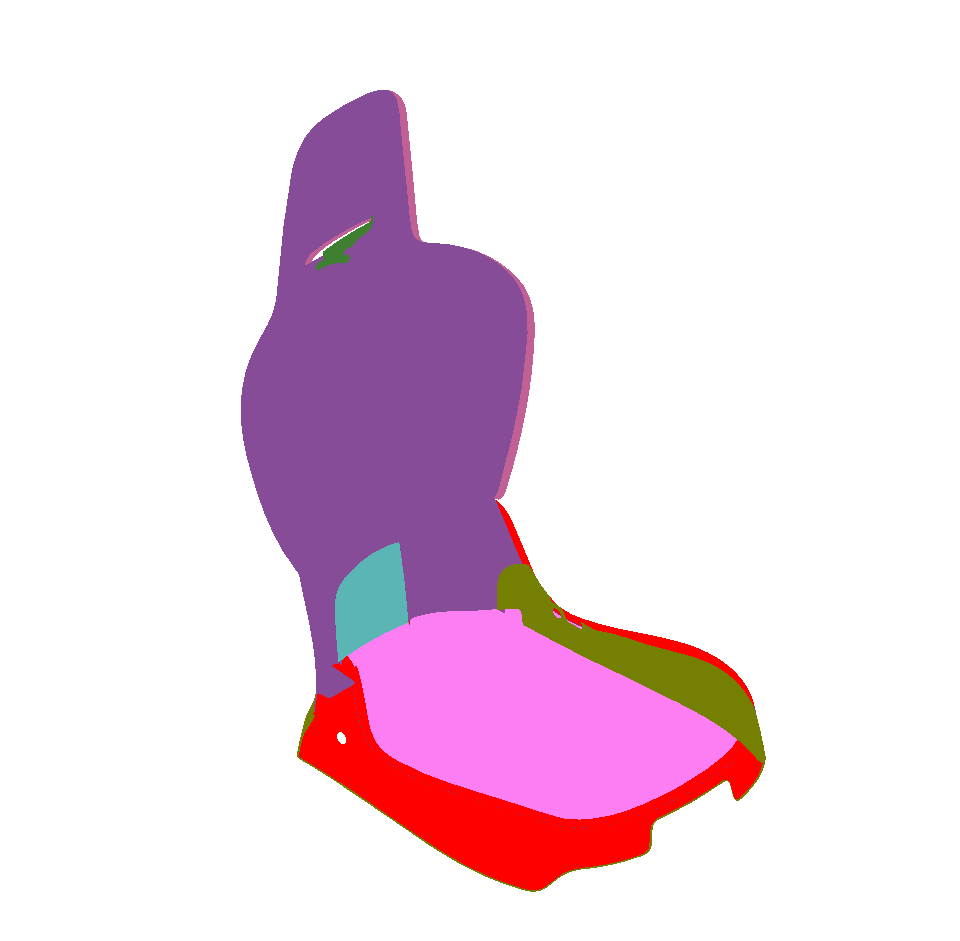
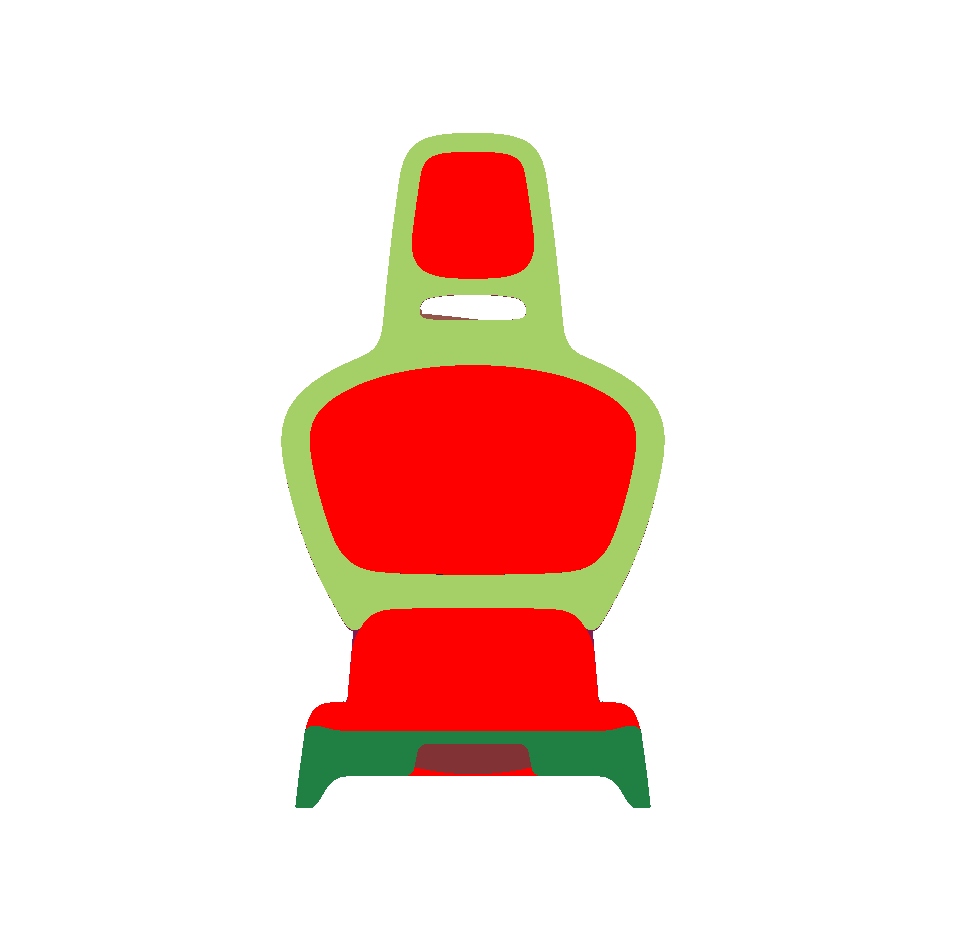
 Selected Surfaces: automatically orients a selection of surfaces. When a set of surfaces is selected, the function determines the corresponding bounding volume. Fourteen renderings of the selected surfaces are performed for camera positions spread around the bounding volume. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Selected Surfaces: automatically orients a selection of surfaces. When a set of surfaces is selected, the function determines the corresponding bounding volume. Fourteen renderings of the selected surfaces are performed for camera positions spread around the bounding volume. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Warning
Only visible pixels are taken into account. If a surface is completely occluded by another surface in the selection, it will never be reversed.
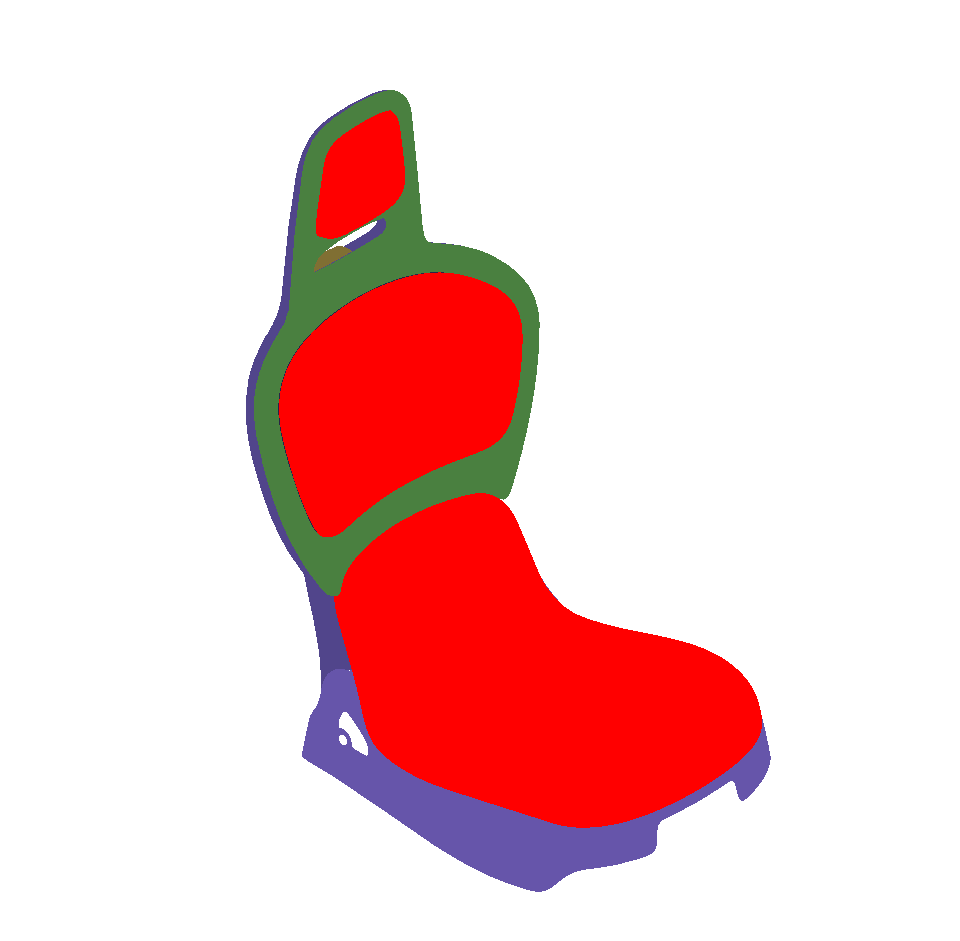
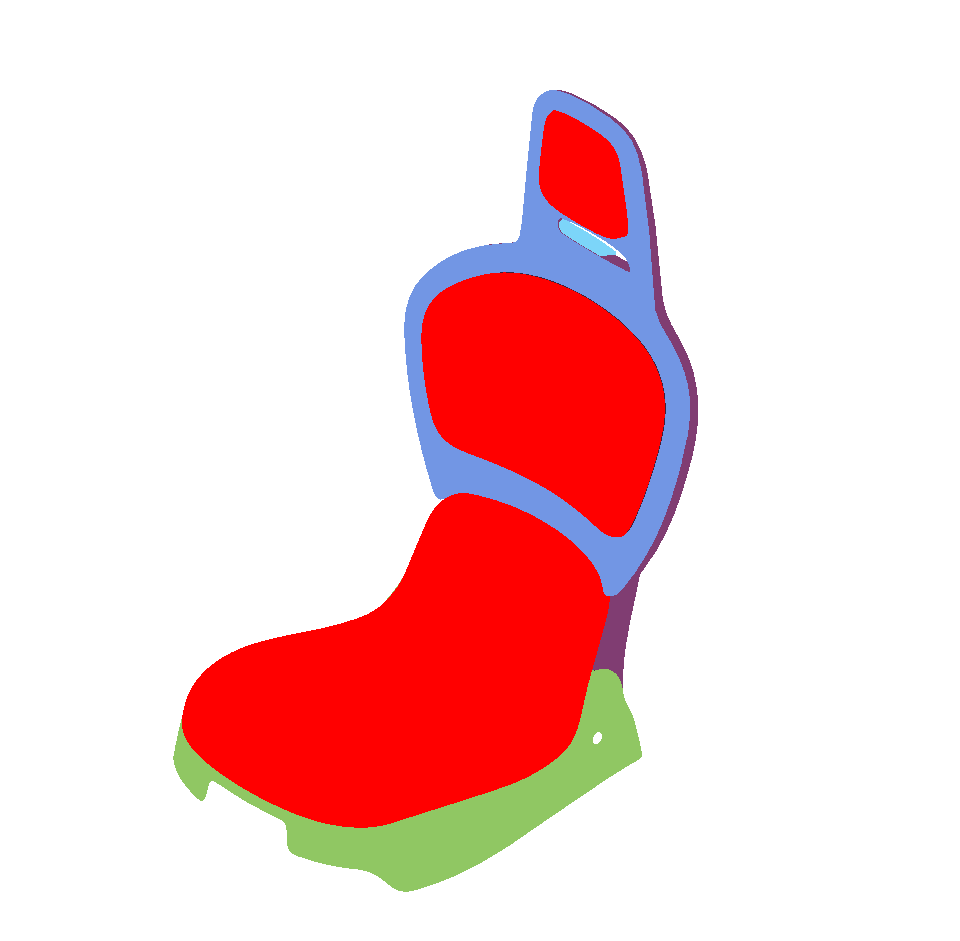
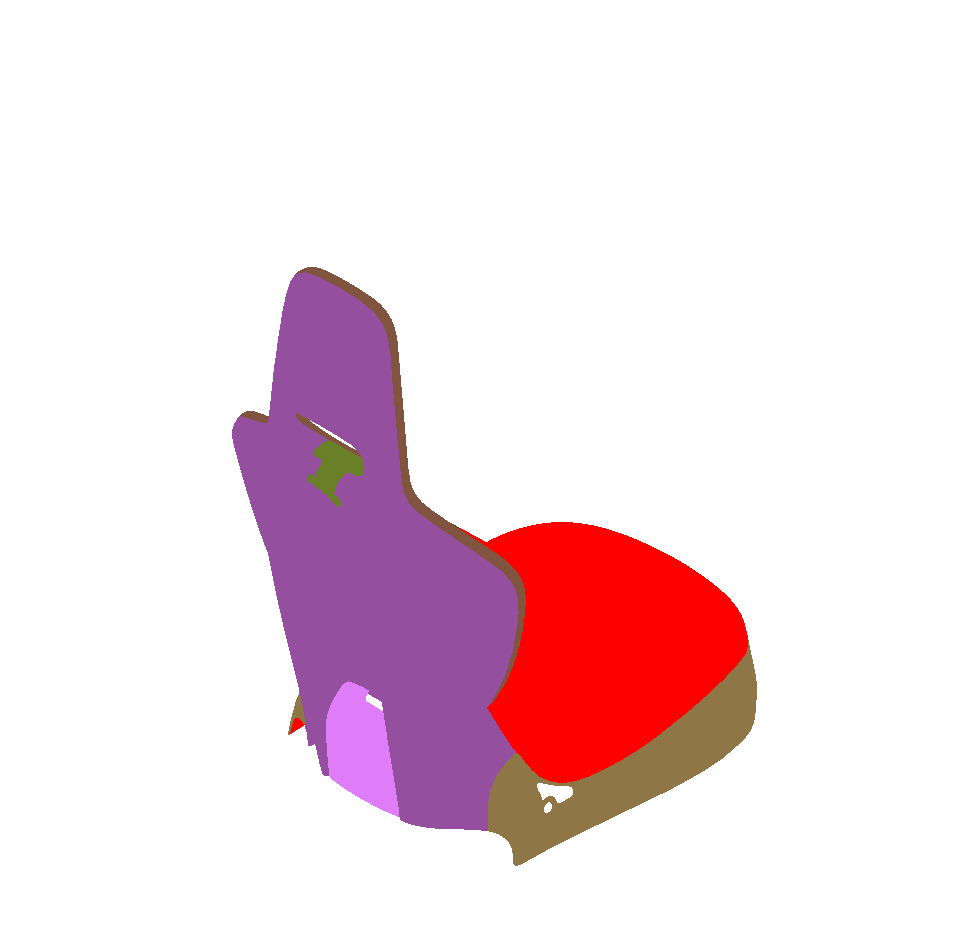
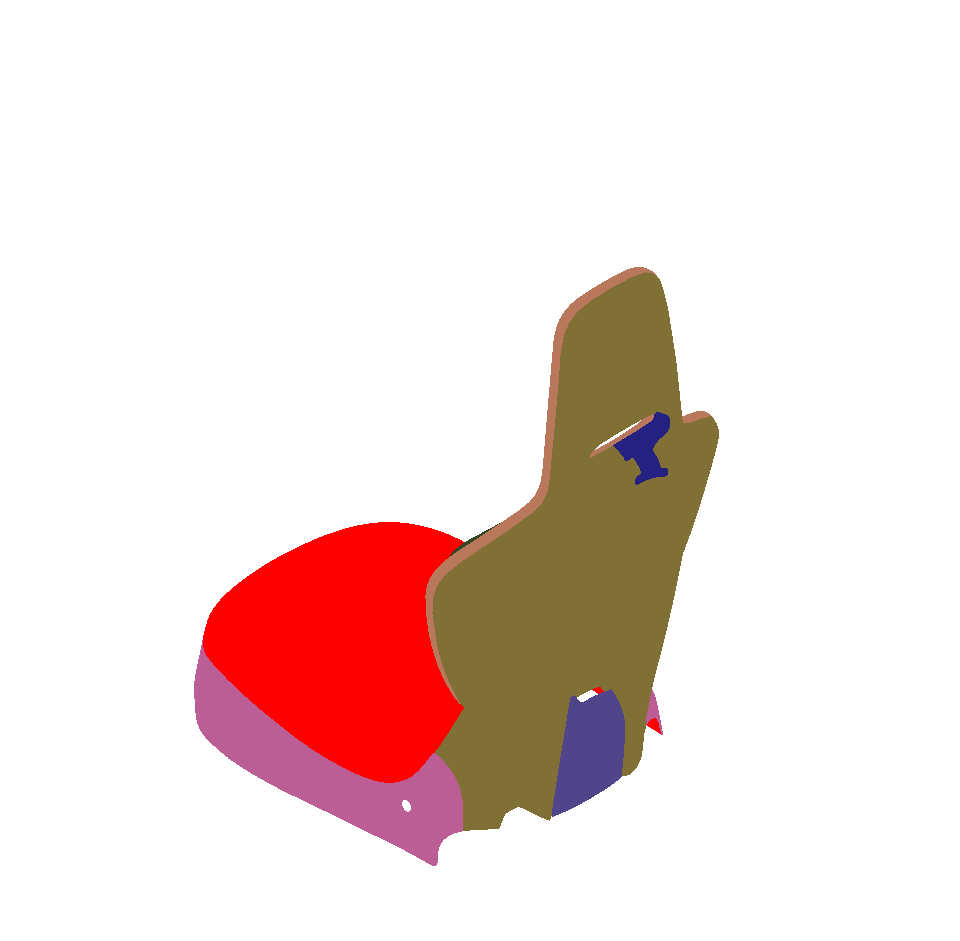
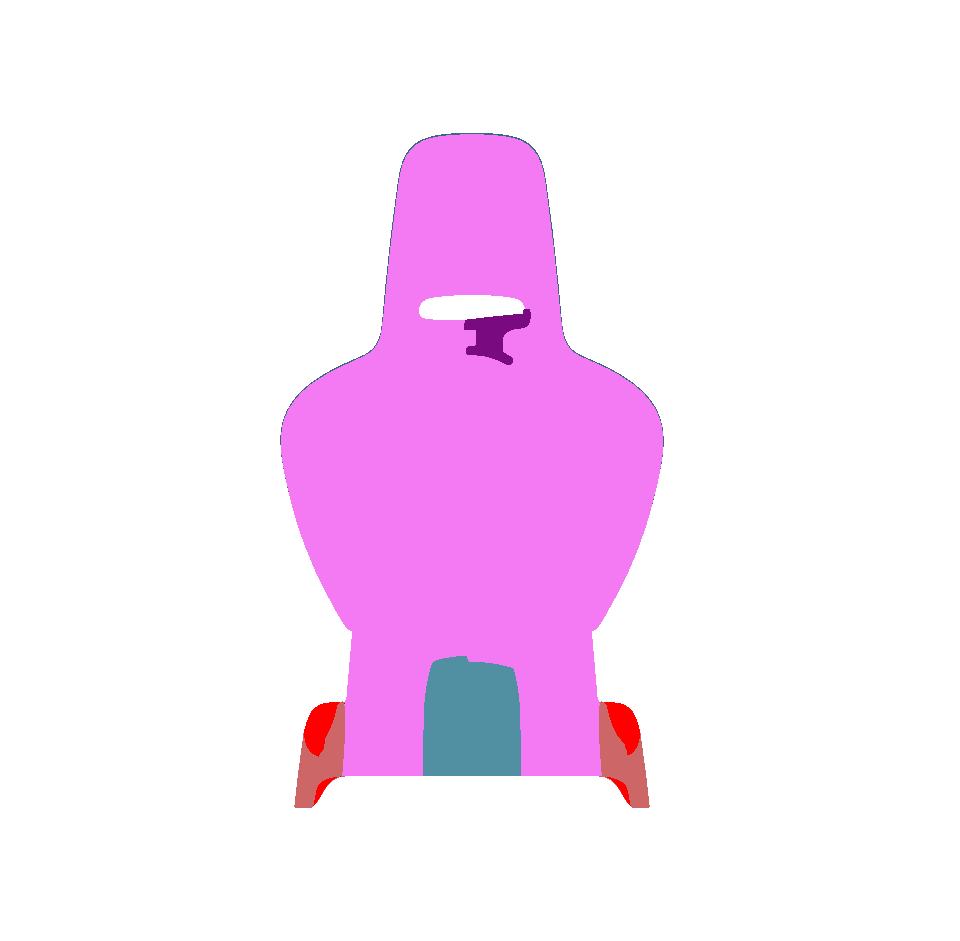
 Surface towards Interior: automatically orients surfaces towards an interior volume. Six renderings taking all the surfaces in the scene into account are performed from the current camera position in the following directions: forward, backward, up, down, left and right. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Surface towards Interior: automatically orients surfaces towards an interior volume. Six renderings taking all the surfaces in the scene into account are performed from the current camera position in the following directions: forward, backward, up, down, left and right. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Warning
As for the auto-orientation function for Selected Surfaces, only visible pixels are taken into account. If a surface is completely occluded by another in the selection, it will never be reversed.
 Visible Surfaces: automatically orients all surfaces visible from the current point of view. In order to determine if the front or the rear face of a surface is visible from this point of view, a rendering is performed. The number of red pixels is compared to the number of pixels of another color among the visible pixels of the surface (i.e. pixels not occluded by another surface). If most pixels are red, the surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Visible Surfaces: automatically orients all surfaces visible from the current point of view. In order to determine if the front or the rear face of a surface is visible from this point of view, a rendering is performed. The number of red pixels is compared to the number of pixels of another color among the visible pixels of the surface (i.e. pixels not occluded by another surface). If most pixels are red, the surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.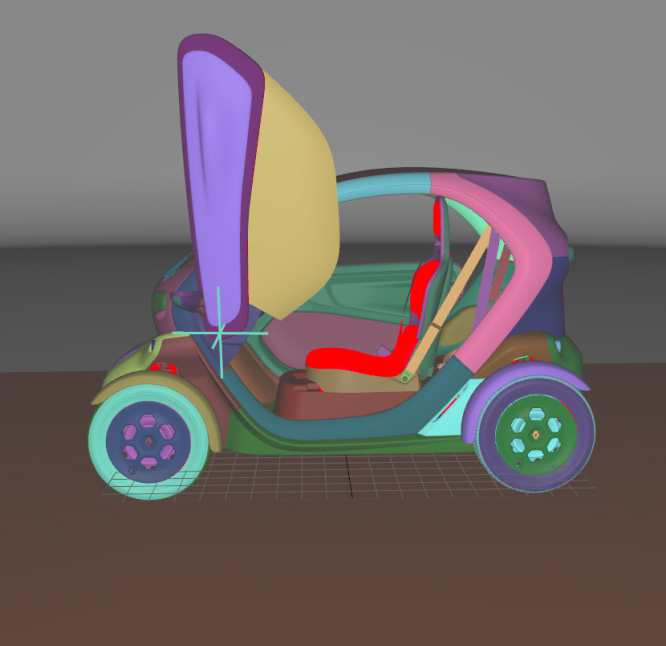
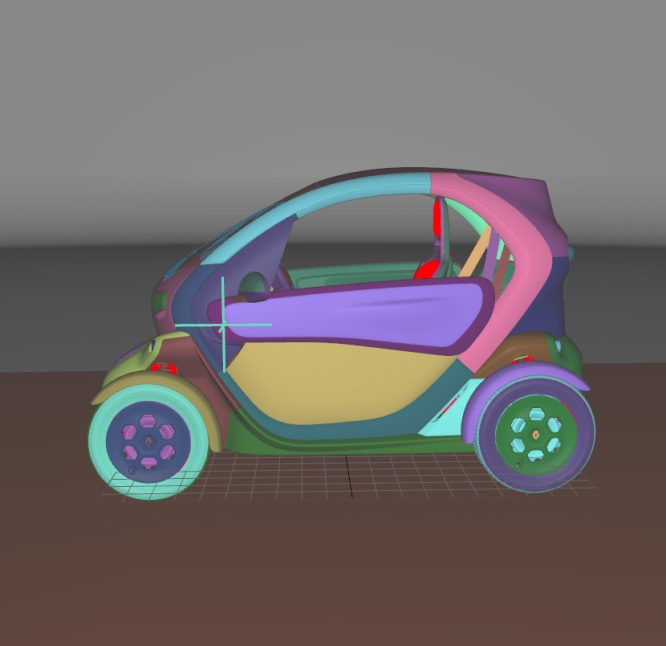
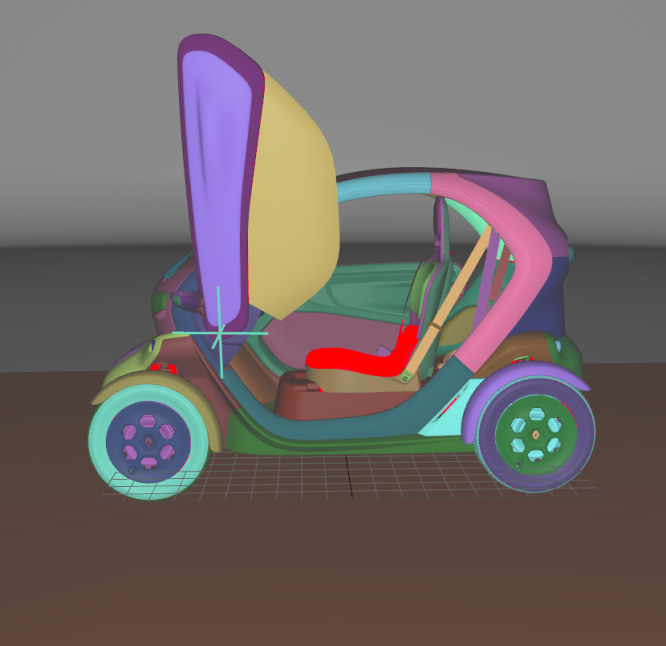
 Selected Surfaces: automatically orients a selection of surfaces. When a set of surfaces is selected, the function determines the corresponding bounding volume. Fourteen renderings of the selected surfaces are performed for camera positions spread around the bounding volume. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Selected Surfaces: automatically orients a selection of surfaces. When a set of surfaces is selected, the function determines the corresponding bounding volume. Fourteen renderings of the selected surfaces are performed for camera positions spread around the bounding volume. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
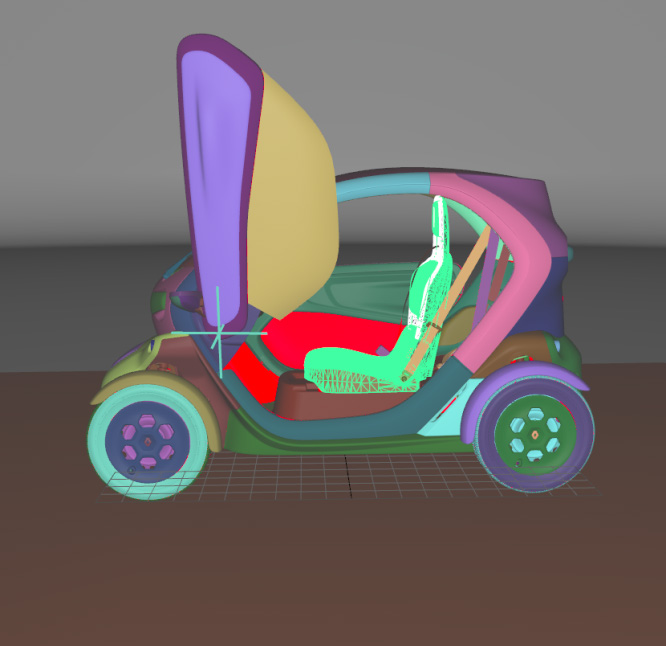
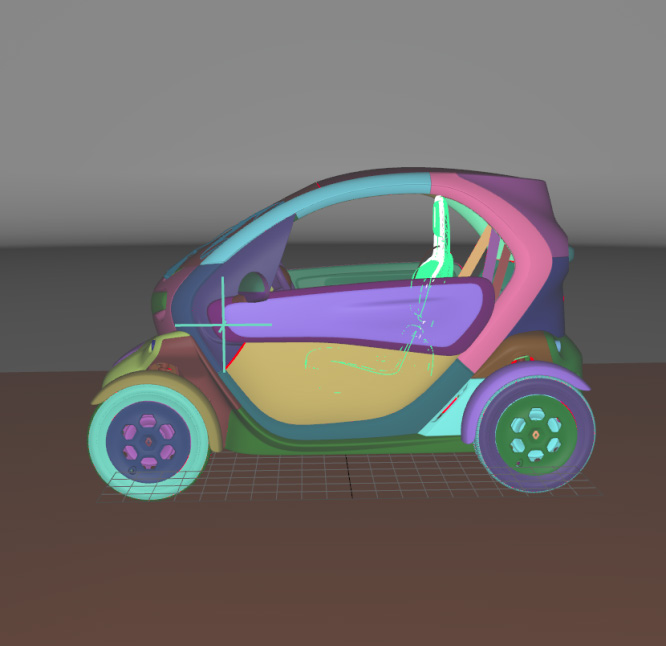
 Surface towards Interior: automatically orients surfaces towards an interior volume. Six renderings taking all the surfaces in the scene into account are performed from the current camera position in the following directions: forward, backward, up, down, left and right. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.
Surface towards Interior: automatically orients surfaces towards an interior volume. Six renderings taking all the surfaces in the scene into account are performed from the current camera position in the following directions: forward, backward, up, down, left and right. If more red pixels than pixels of another color are visible for a given surface, this surface is considered to be inside out and its orientation is flipped.