Manipulating Surfaces
Gizmos
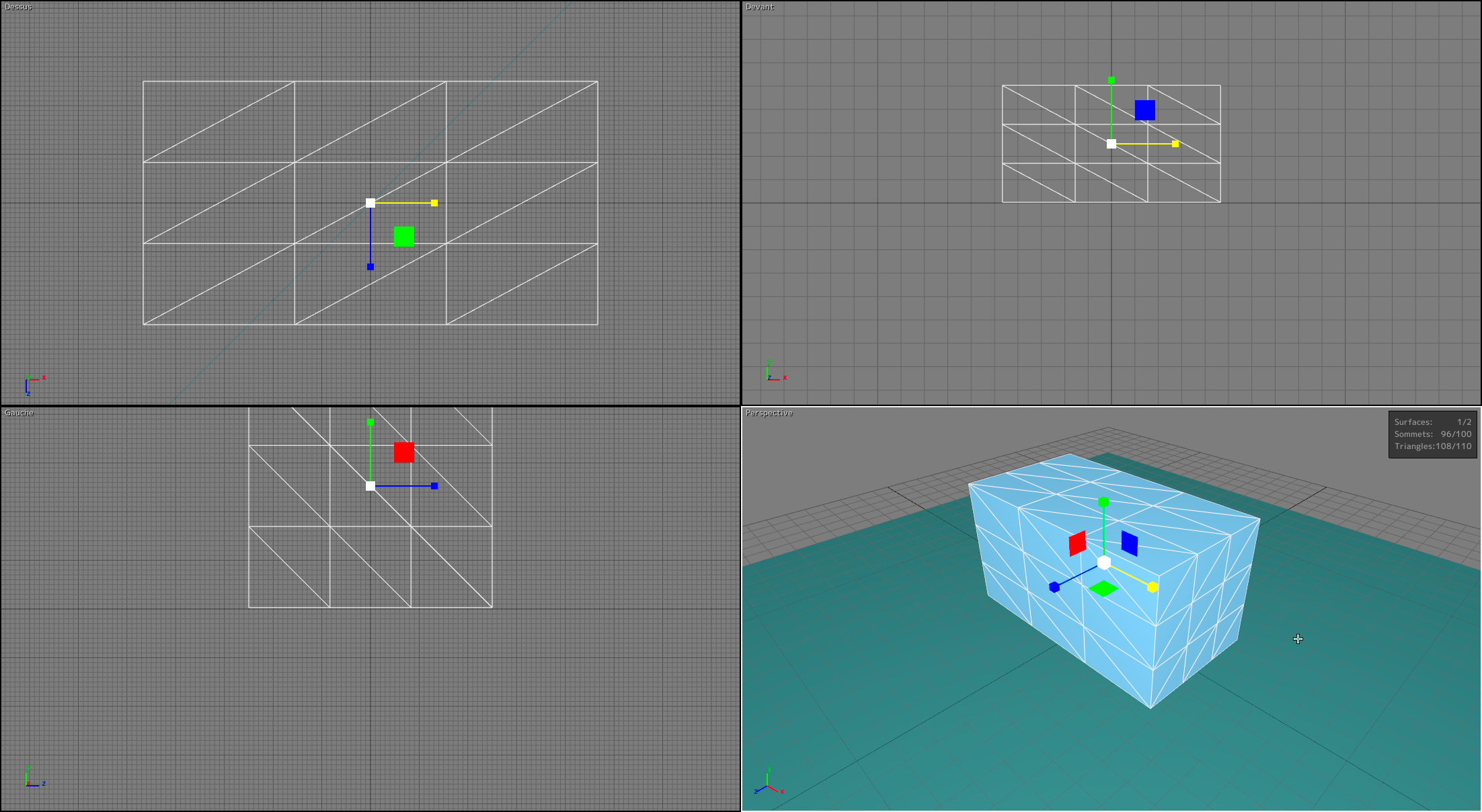
Patchwork 3D includes gizmos that make it easier to manipulate 3D objects in space. They appear automatically as an overlay on the selected as soon as the gizmo of Translation  , Rotation
, Rotation  or
or  Scale is enabled.
Scale is enabled.
To move an element along an axis, click the part of the gizmo that represents the movement axis and drag the mouse in the desired direction. To rotate an element, the movement axis is either up-down or left-right. The farther you drag the mouse along this axis, the greater the angle of rotation will be.
The operation is the same for both types of movement (translation and rotation) and for scaling:
If it is a single selection, the movement or scaling will be done in its transformation frame.
If it is a multiple selection, two options are possible depending on the chosen mode:
each modification (movement or scaling) will be done in the leader's frame,
each modification (movement or scaling) will be done in its own frame.
Tip
When you hold down the Alt key, the selected element moves at a preset pitch. The value of this pitch can be customized (see the section on setting step values in the chapter Positioning Surfaces from the Main Interface.
A numerical indicator placed close to the gizmo shows the value applied to transformation in real-time.
 Translation movement | 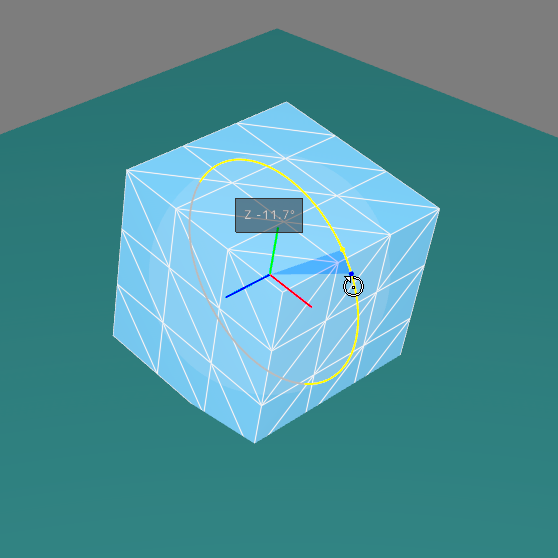 Rotation movement | 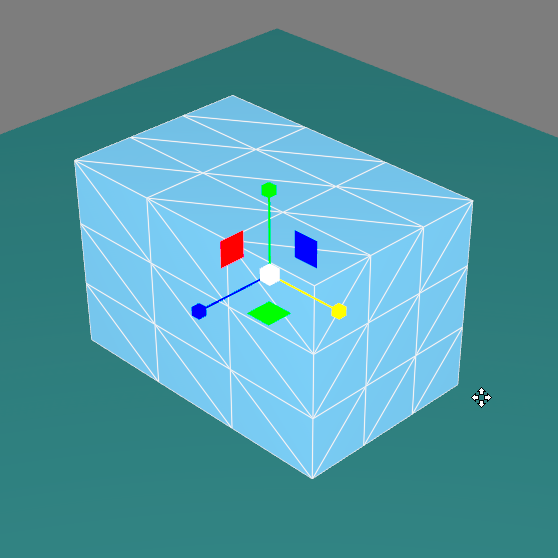 Scaling |
Translation
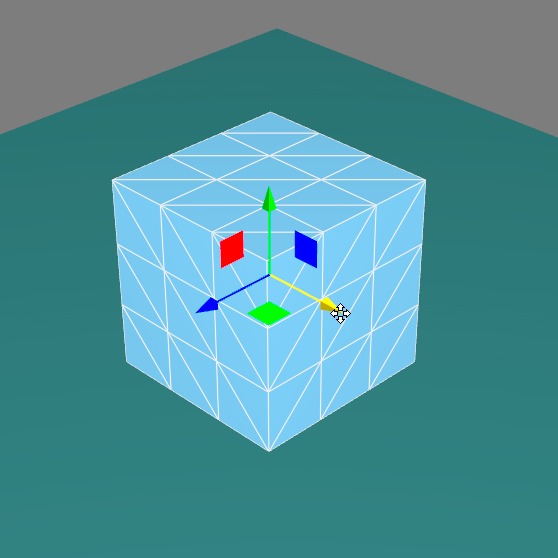
The translation gizmo  lets you move surfaces by clicking + dragging on the selection.
lets you move surfaces by clicking + dragging on the selection.
Translation Gizmo.
Rotation
The rotation gizmo  allows the orientation of surfaces to be modified by clicking and dragging the selection. This operational mode works similarly to the translation gizmo: you can modify the selection with the same mouse and keyboard combinations.
allows the orientation of surfaces to be modified by clicking and dragging the selection. This operational mode works similarly to the translation gizmo: you can modify the selection with the same mouse and keyboard combinations.
When the mouse is moved along an axis (up-down or left-right), the selected surfaces rotate around one of the axes of their referential.
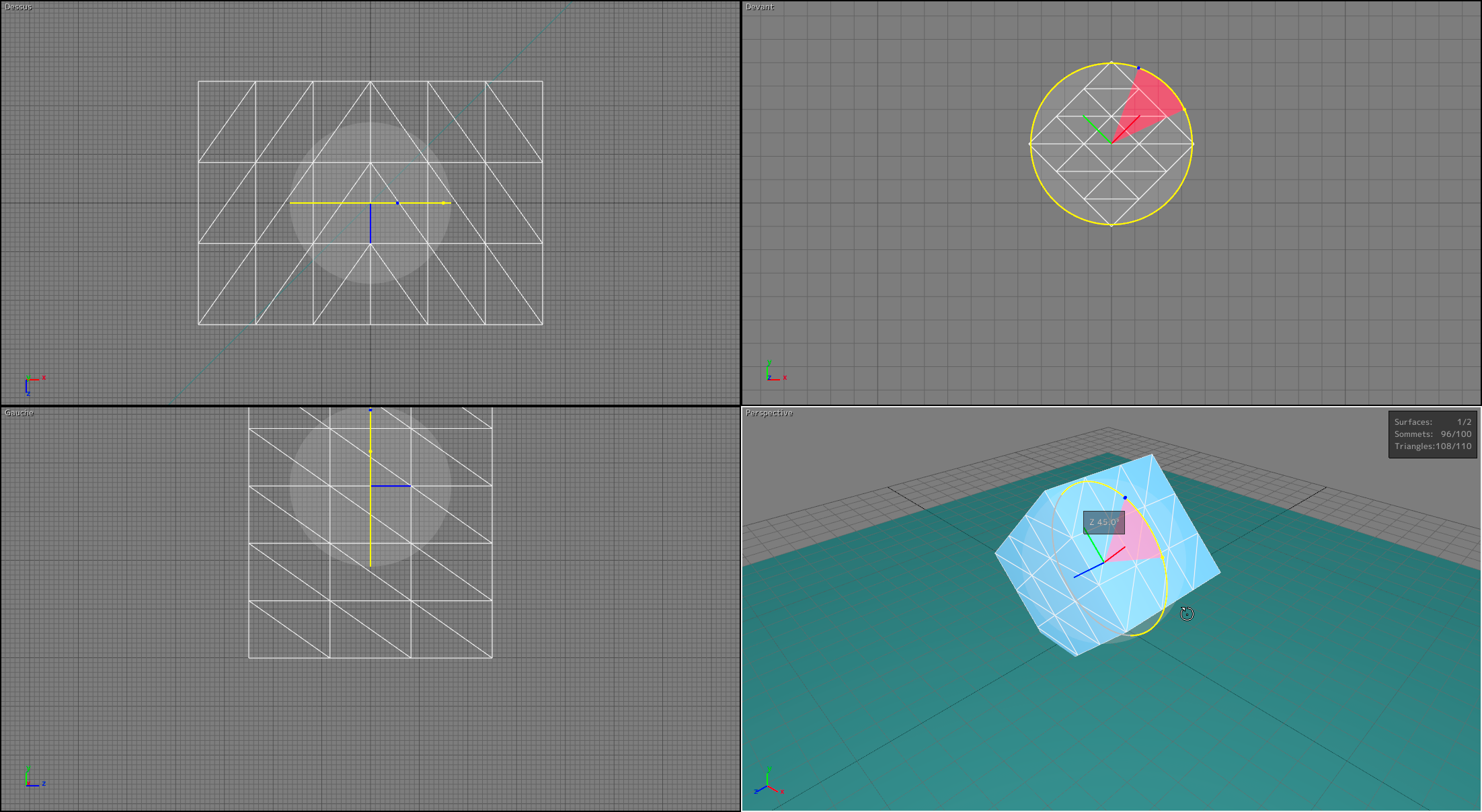
Rotation Gizmo.
Scaling
The scaling gizmo  allows you to resize the selected surfaces by clicking + dragging on:
allows you to resize the selected surfaces by clicking + dragging on:
the axis of the gizmo, the resizing of the surfaces will then be constrained to the selected axis (X, Y, or Z).
the plane of the gizmo, the resizing of the surfaces will then be constrained to the selected plane (horizontal, vertical, transverse).
the central cube, the resizing of the surfaces will be uniform on the 3 axes at the same time.
A surface is moved in relation to its transformation referential. The center of the referential is placed over the surface's pivot.

Translation Gizmo.
Transformation Tools
The drop-down menu in the top toolbar establishes the transformation referential and contains four options: Screen, View, World and Local.
Referential option | Description |
|---|---|
Screen | The transformation referential is aligned with that of the screen on the XY plane. Moving a surface in XY occurs on a plane parallel to the screen and passing through the surface's pivot. |
View | For orthographic views (top, bottom, left, right, front, and back), the behavior is the same as for the Screen orientation. For isometric and perspective views, the behavior is the same as the World orientation. |
World | The transformation referential is aligned with the axes of the model. |
Local | The transformation referential is aligned with the local referential of the surface. In this mode, the transformation referential is identical to the pivot. |
Moving a surface occurs in three dimensions along the transformation referential, although the cursor is moved on the plane of the screen in two dimensions. The movement of the mouse is therefore not sufficient to determine the 3D movement of a surface. This is why moving a surface is limited to one or two selected dimensions via the transformation referential.
Surface Visibility and Frozen States
Shaper provides three operating modes that allow you to quickly modify the visibility and the frozen state of surfaces:
Icon | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Click to Hide | Click on a surface to hide it. |
| Click to Freeze | Click on a surface to freeze it. |
| Click to Unfreeze | Click on a surface to unfreeze it. |