Diffuse
Light does not pass through a diffuse layer. Light is either absorbed, or returned to the eye of the observer. The Diffuse tab groups the settings related to this diffuse layer.
Diffuse Color
The color of the diffuse layer is influenced by several settings: the color Filter, the lighting environment conditions, the ambient color, and the illumination color, among others.
The color Filter setting corresponds to the color perceived when the material is lit by white light. As the material reacts like a filter, it reflects part of the light it receives. The perceived color of an object is thus greatly influenced by the lighting environment. If we consider that white light is made up in equal parts of green, red and blue (empirical computer model), then a black body absorbs all these components, a white body reflects them without alteration, a red body absorbs the green and blue, etc.
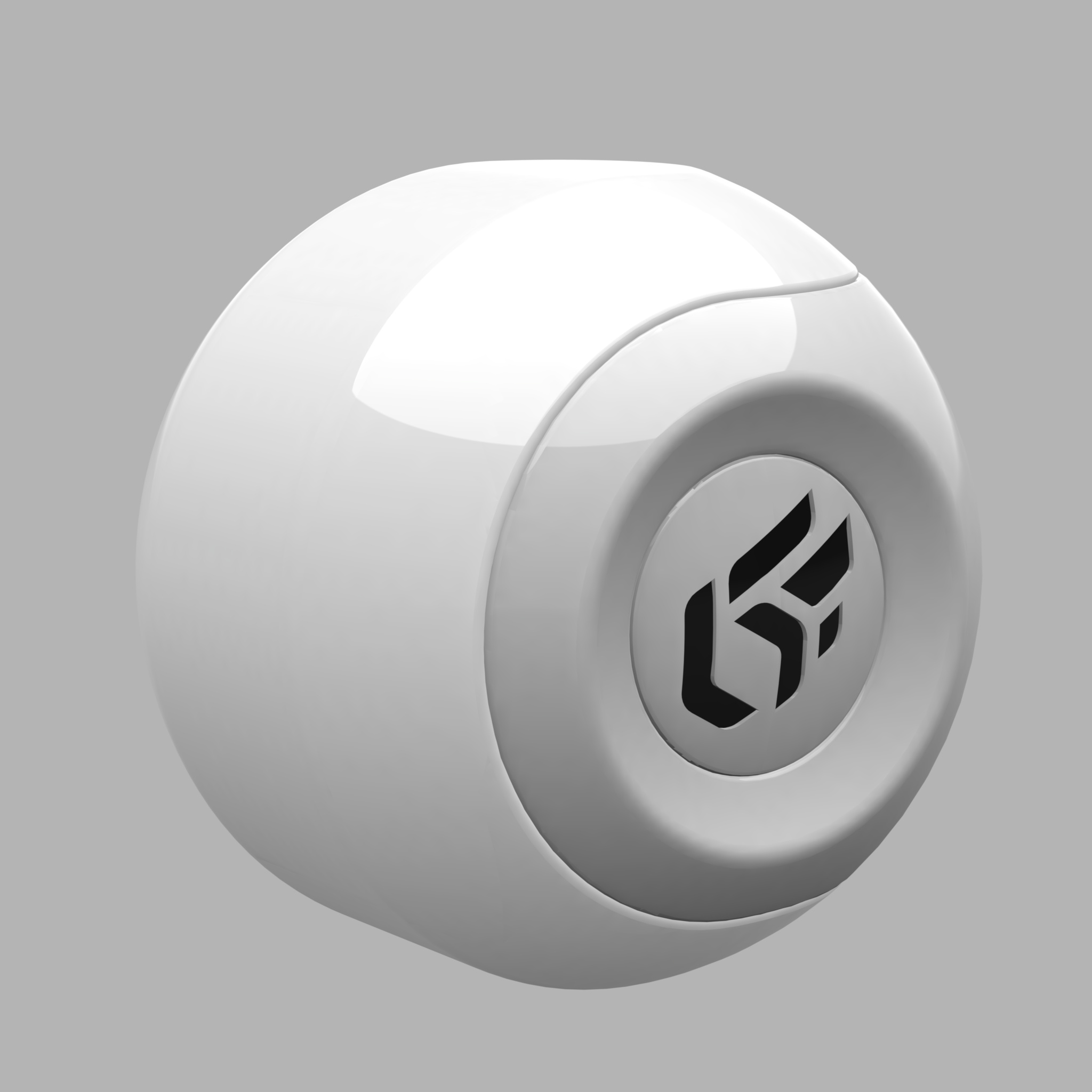 |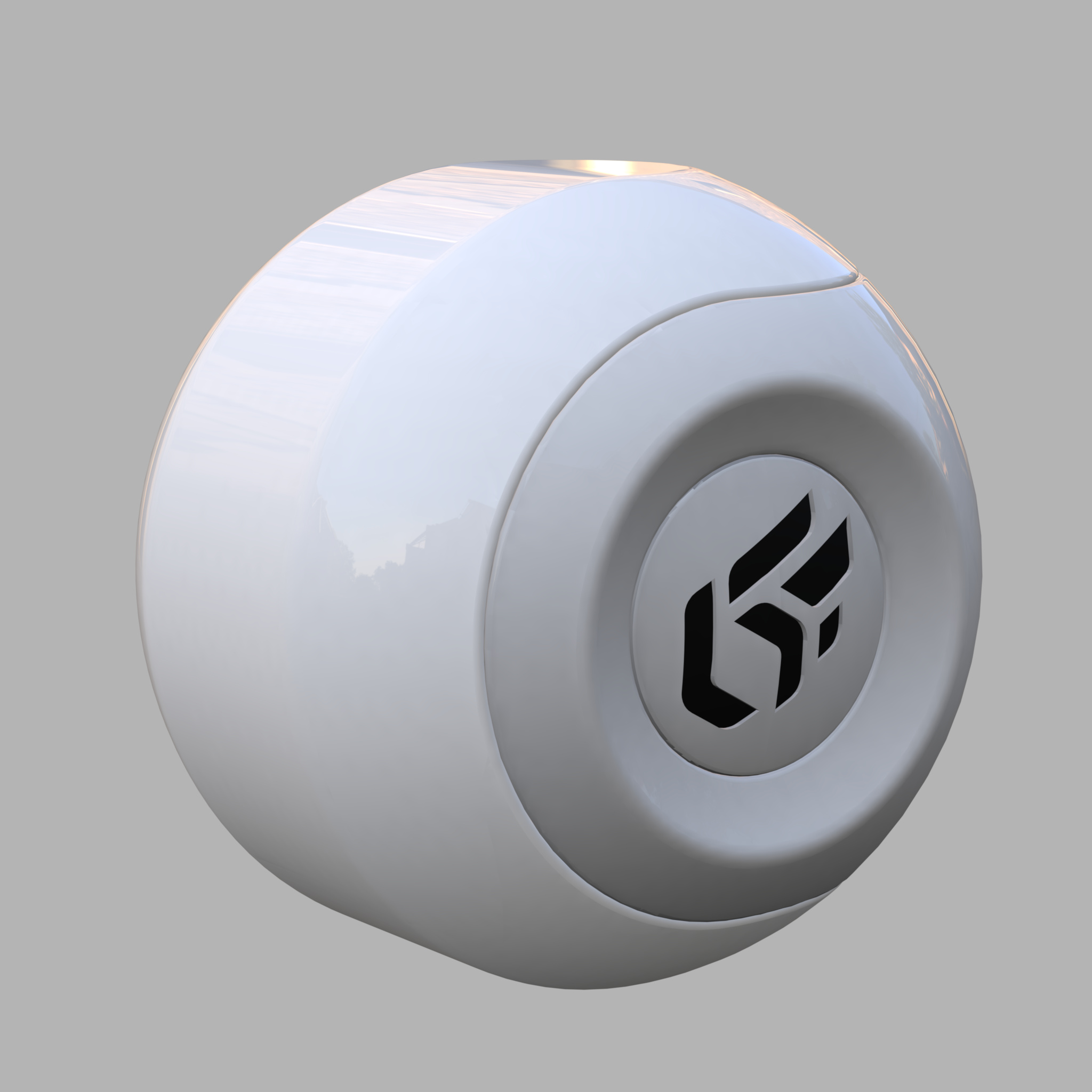  |  |
Influence of the lighting environment conditions on the color of a material.
The creation of a new material should thus imperatively be performed in a neutral light environment, for example, the default environment in the Matter module.
The Intensity parameter allows you to amplify by a multiplication factor the effect of the lighting environment on the material.
The Ambient color parameter allows you to add a constant color. It is common practice to add a light gray to lighten a material. However, we would advise you to limit the amount of ambient light since a material of relatively dull appearance originates from a relatively dull environment.
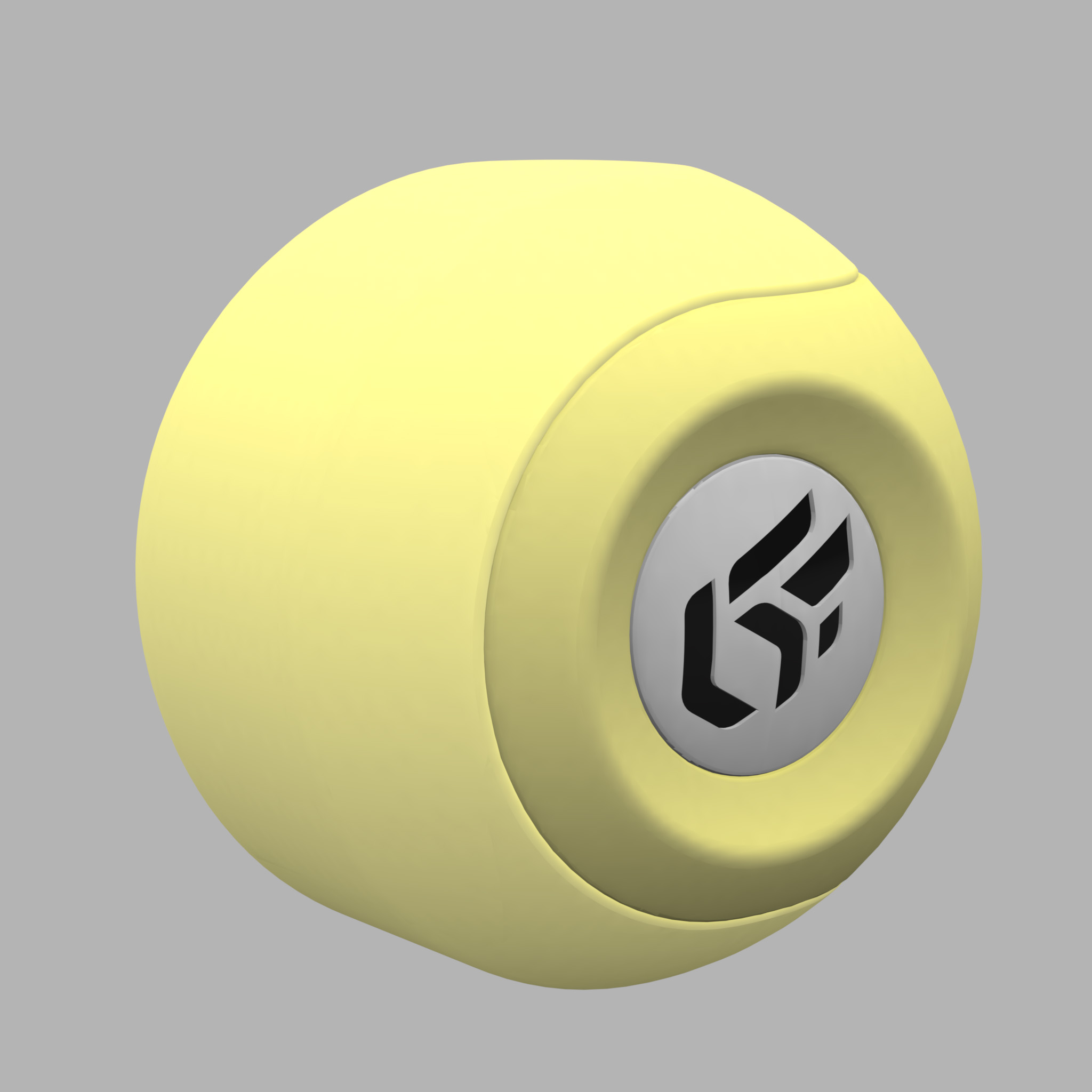 |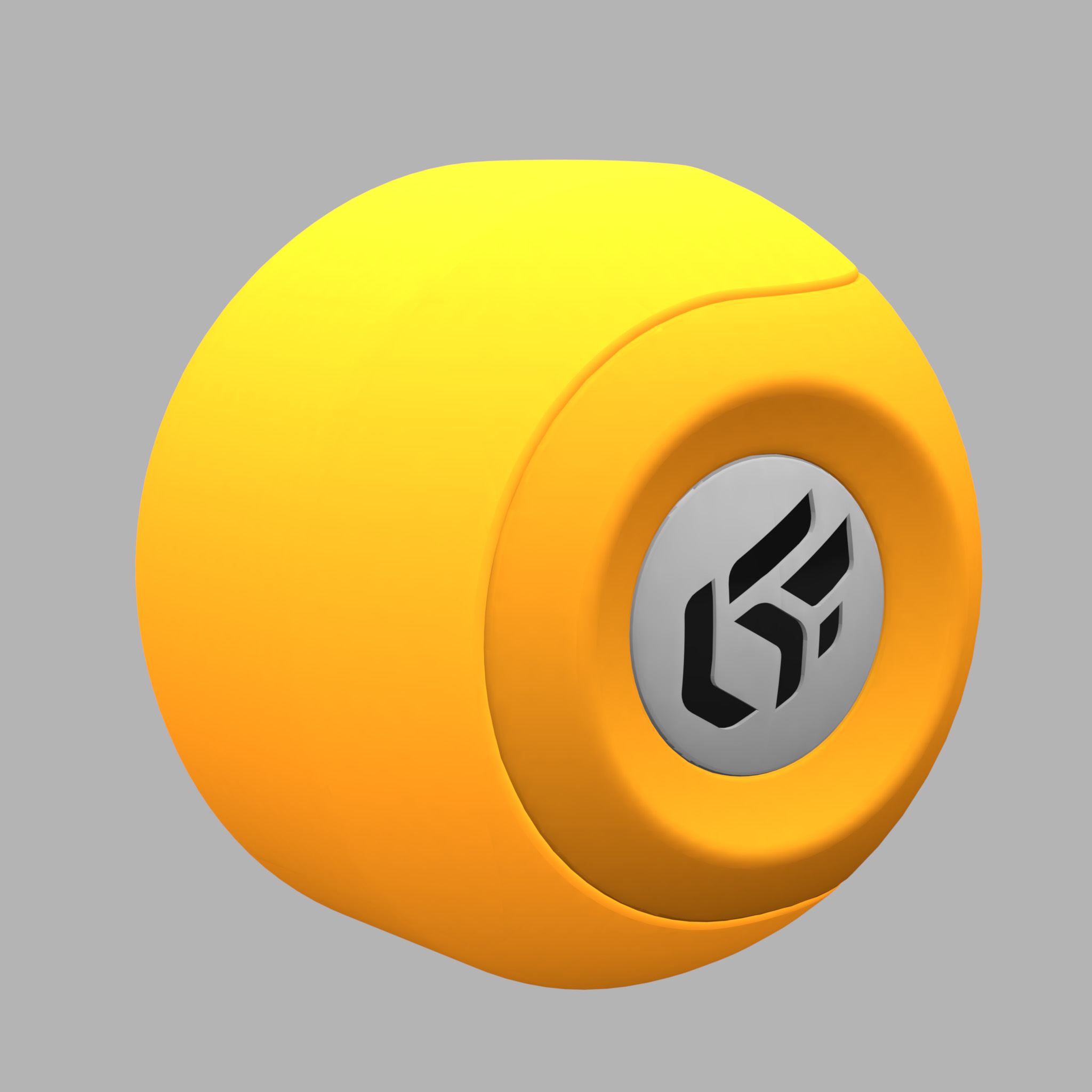  |
The effect of an ambient color on the appearance of a yellow material. Left: gray ambient color. Right: red ambient color.
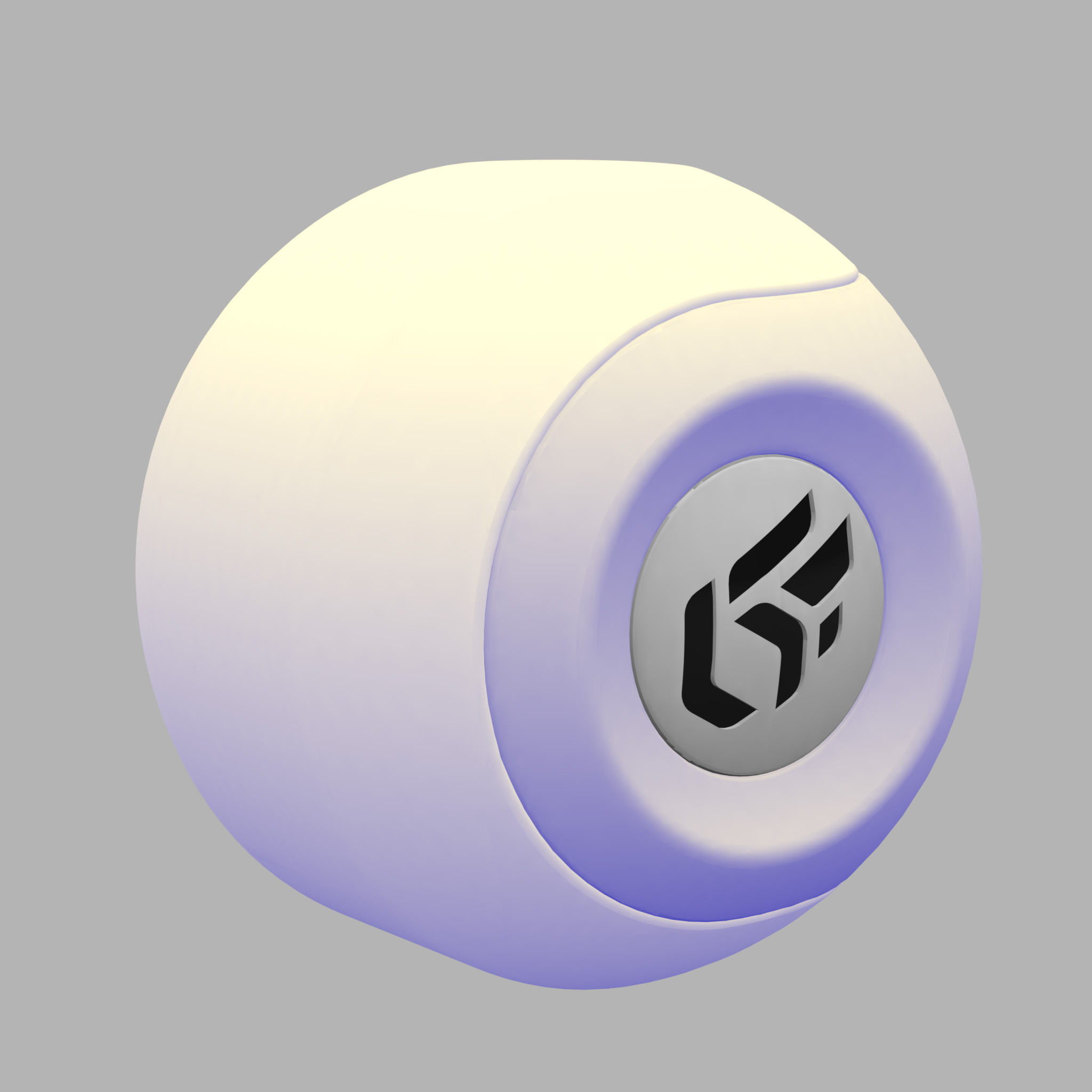 |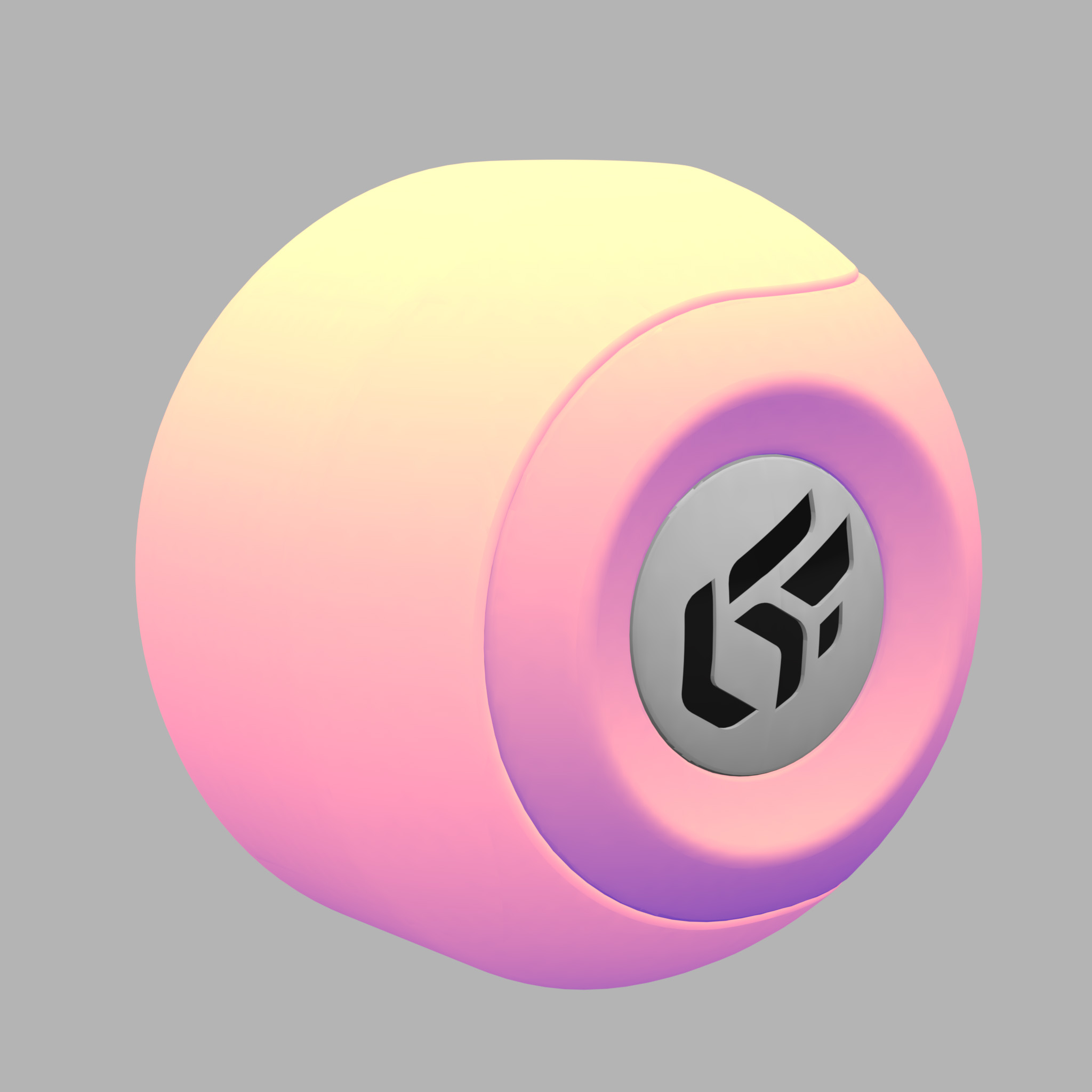  |
The effect of an illumination color on the appearance of a yellow material. Left: ambient gray color + blue illumination color. Right: ambient color red + illumination color blue.
Color Map
Some materials have a pattern or motif that is created by repeating an image across the surfaces to which the material is assigned. The Color Map settings are used to assign, resize, and position the first instance of such an image.
Color maps are image or video textures. To use a texture as a color map, drag it from the sidebar texture library and drop it in the color map zone. To be shown, the color map must also be enabled by ticking the checkbox next to the color map zone.
The texture dimensions are used by default for an image texture.
For a video texture, the longest edge of the format is scaled to one meter by default. The format's aspect ratio is respected.
Any texture used as a color map will repeat.
You will find in the accordion menu named Mapping the following parameters Allow repeat in U and Allow repeat in V that allow you to choose to repeat the texture in U and/or V.
By checking the Mirrored checkbox you can reflect the texture in U and/or V.
Transparency of the Diffuse Layer
The transparency of a standard material of the Diffuse or Diffuse and Reflection classes can be adjusted directly fromthe Materials Editor using the Opacity modulator:
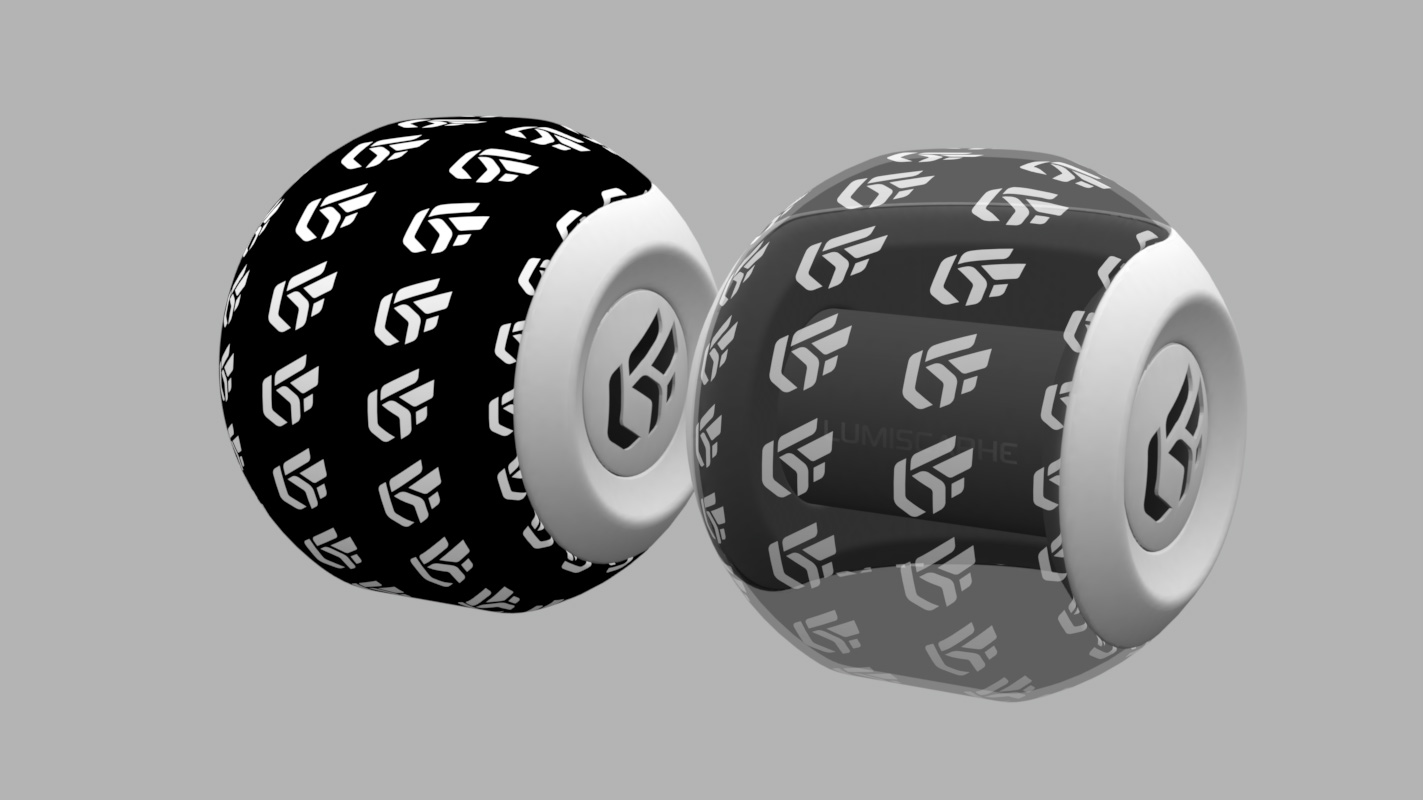

The Transparency accordion menu lets you use a texture for controlling the transparency of the material. The alpha layer contained in the images (PNG format) is used to define the transparency of the texture.
If the texture used as image alpha does not have an alpha layer (JPG image), it is the luminosity of the image that is used as the alpha layer. In this case, check Use color map transparency. The darkest colors correspond to the most transparent areas:
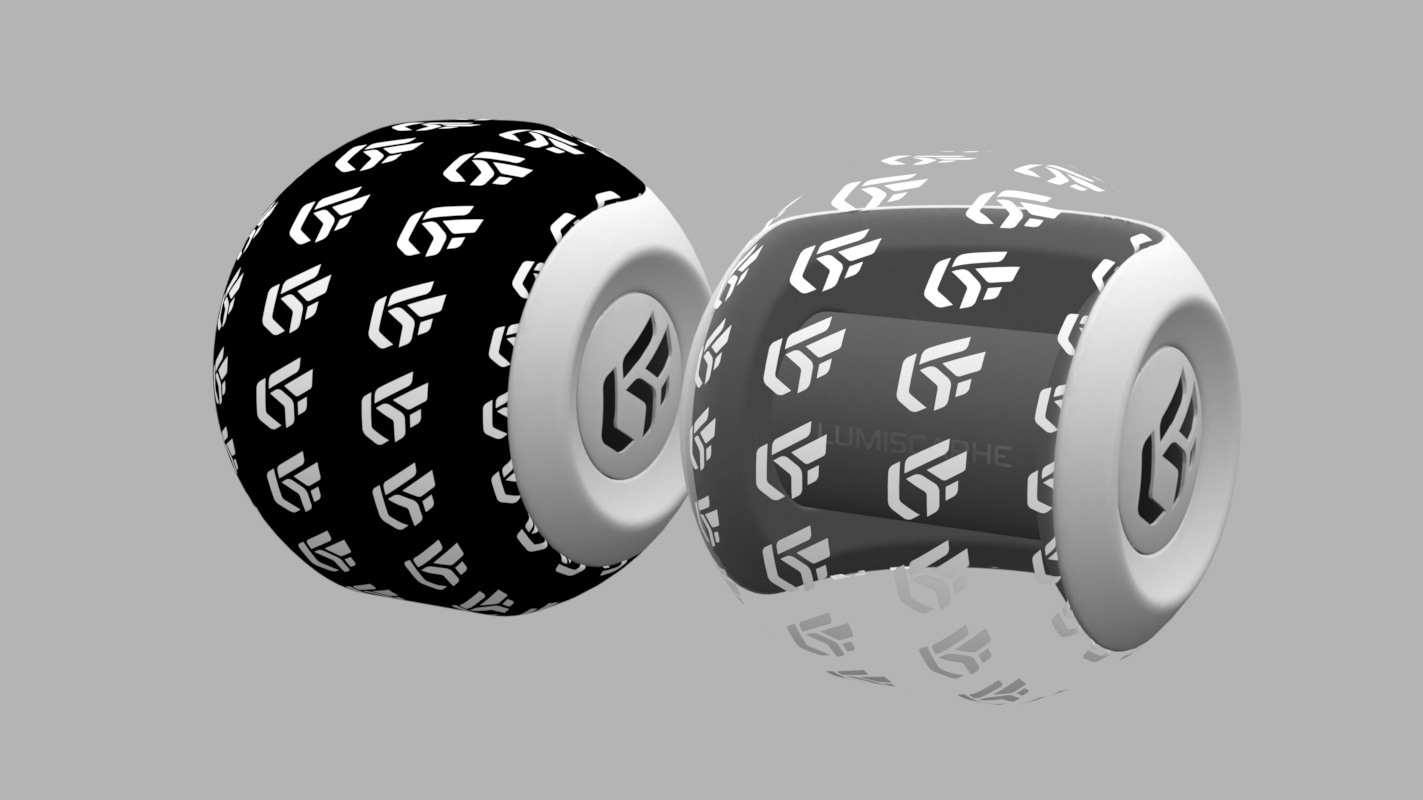

You will find in the accordion menu named Mapping the following parameters Allow repeat in U and Allow repeat in V that allow you to choose to repeat the texture in U and/or V.
By checking the Mirrored checkbox you can reflect the texture in U and/or V.
Filter According to View Angle
Some materials have a color that changes according to the angle of observation. This effect is implemented using a gradient ramp. Click on the Gradient  Editor button from the accordion menu called Advanced in order to modify the gradient that is used.
Editor button from the accordion menu called Advanced in order to modify the gradient that is used.